The greenhouse effect is a natural process by which certain gases in the Earth's atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor, and methane, trap heat from the sun and warm the planet's surface. These gases are called greenhouse gases because they act like the glass walls of a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to enter and trapping the heat inside.
Without the greenhouse effect, the Earth's average temperature would be much colder and life as we know it would not be possible. However, human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, have caused an increase in the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, leading to an enhanced greenhouse effect and global warming. This is because the extra greenhouse gases trap more heat, causing the Earth's average temperature to rise, which can have significant impacts on the planet's climate and ecosystems.
The greenhouse effect is named after the way in which a greenhouse traps heat. In a greenhouse, sunlight enters through the glass roof and walls and heats up the air and the plants inside. However, the heat cannot escape as easily as it entered, and so the temperature inside the greenhouse rises.
Similarly, the greenhouse effect refers to the way in which certain gases in the Earth's atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide and methane, act like the glass walls of a greenhouse. These gases allow sunlight to enter the Earth's atmosphere and warm the planet's surface, but they also trap some of the heat that is radiated back into space. This trapped heat causes the temperature of the planet to rise, much like the temperature inside a greenhouse.
The term "greenhouse effect" was first used by scientists in the early 1900s to describe this phenomenon, and it has since become a widely recognized concept in the study of climate change.
The greenhouse effect can have both positive and negative effects on the Earth's climate and environment. Here are some of the effects:
Positive effects: The greenhouse effect is responsible for keeping the Earth's temperature at a level that can support life. Without it, the Earth would be too cold for life to exist as we know it.
Negative effects: The excessive release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, primarily from human activities such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, has caused an intensification of the natural greenhouse effect. This enhanced greenhouse effect is leading to global warming and climate change, with negative consequences such as:
Rising sea levels due to the melting of glaciers and polar ice caps
Increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts
Changes in precipitation patterns, which can lead to water scarcity and crop failure
Impacts on biodiversity and ecosystems due to changes in temperature and rainfall patterns
Overall, the negative effects of the enhanced greenhouse effect are far greater than any potential positive effects. This is why it is crucial to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate the effects of climate change and protect the planet.
Greenhouse gases are harmful because they trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, which leads to an increase in the Earth's temperature. This increase in temperature can have a range of negative impacts on the planet, including:
Climate change: The increase in temperature caused by greenhouse gases leads to climate change, which can have severe impacts on the environment and human societies.
Extreme weather events: The increased temperature can lead to more frequent and severe heatwaves, droughts, hurricanes, and other extreme weather events.
Rising sea levels: As the Earth's temperature increases, the polar ice caps and glaciers melt, which causes the sea level to rise. This can lead to flooding and the loss of land.
Ocean acidification: As the levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increase, more of it dissolves into the ocean, leading to acidification of the water. This can have negative impacts on marine life and the food chain.
Health impacts: Increased air pollution caused by the burning of fossil fuels, which release greenhouse gases, can have negative impacts on human health, including respiratory problems, heart disease, and cancer.
In summary, greenhouse gases are harmful because they disrupt the Earth's natural systems and have negative impacts on the environment and human societies. It is important to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate these harmful effects and protect the planet.
The main greenhouse gases are:
Carbon dioxide (CO2): This is the most important greenhouse gas and is responsible for about 63% of the total warming effect of all greenhouse gases. Carbon dioxide is primarily produced by the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas.
Methane (CH4): This is the second-most important greenhouse gas and is responsible for about 16% of the total warming effect of all greenhouse gases. Methane is produced by natural sources such as wetlands and by human activities such as livestock farming, rice cultivation, and landfills.
Nitrous oxide (N2O): This is another important greenhouse gas and is responsible for about 6% of the total warming effect of all greenhouse gases. Nitrous oxide is primarily produced by human activities such as agriculture and the burning of fossil fuels.
Fluorinated gases: These are a group of synthetic gases that are used in a variety of industrial and commercial applications such as refrigeration and air conditioning. They are much less abundant than the other greenhouse gases but have a much greater warming effect per molecule.
The concentration of these greenhouse gases in the atmosphere has been increasing due to human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and agriculture. This increase in greenhouse gases is causing the Earth's temperature to rise and leading to climate change.

The three main causes of global warming are:
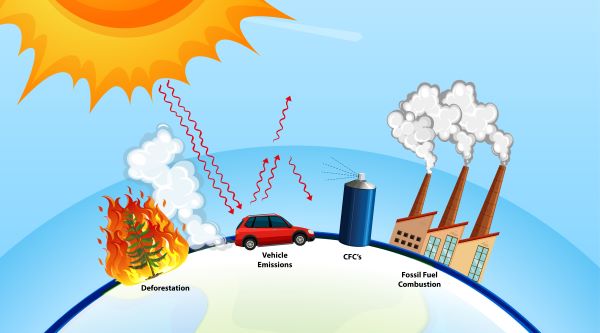
Human activities: The primary cause of global warming is the increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which is primarily caused by human activities such as burning fossil fuels (coal, oil, and gas), deforestation, and industrial processes. These activities release large amounts of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, which trap heat and cause the Earth's temperature to rise.
Natural factors: While human activities are the primary cause of global warming, natural factors such as volcanic eruptions, changes in solar radiation, and variations in the Earth's orbit and tilt can also contribute to changes in the Earth's temperature.
Feedback mechanisms: As the Earth's temperature rises, it can trigger feedback mechanisms that further accelerate global warming. For example, as ice caps and glaciers melt, they reflect less sunlight back into space and absorb more heat, which further accelerates the melting. Similarly, as permafrost in the Arctic melts, it releases large amounts of methane, which is a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere.
Overall, the main cause of global warming is the increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which is primarily caused by human activities.
The greenhouse effect is important because it plays a crucial role in regulating Earth's temperature and making the planet habitable for life as we know it. Without the greenhouse effect, Earth's average temperature would be about -18°C (0°F) instead of its current average temperature of about 15°C (59°F).
The greenhouse effect works by trapping some of the sun's energy in the Earth's atmosphere. Gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor in the atmosphere absorb the sun's energy and then re-radiate it back to the surface. This process helps to keep the Earth's surface warm enough for life to thrive.
However, human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, have increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This increase in greenhouse gases is causing the Earth's temperature to rise, leading to global warming and climate change. Therefore, while the greenhouse effect is important, it's also important to manage and mitigate the amount of greenhouse gases that we release into the atmosphere to prevent further warming of the planet.
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that helps to regulate the Earth's temperature and make the planet habitable. However, human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes, have caused an increase in the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, leading to global warming and climate change. Here are some ways to prevent or reduce the greenhouse effect:
Reduce greenhouse gas emissions: The most effective way to prevent the greenhouse effect is to reduce the amount of greenhouse gases we emit into the atmosphere. This can be achieved by using cleaner energy sources, such as renewable energy, improving energy efficiency, reducing waste, and promoting sustainable transportation.
Support policies and regulations: Governments can implement policies and regulations to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, such as carbon taxes, cap and trade systems, and renewable energy mandates.
Plant trees and restore ecosystems: Trees and other vegetation absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in their tissues. Therefore, planting trees and restoring ecosystems can help to reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Use energy-efficient products: Using energy-efficient products and appliances, such as LED light bulbs and Energy Star certified appliances, can reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
Support research and innovation: Research and innovation can help to develop new technologies and solutions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change.
It's important to remember that preventing the greenhouse effect requires a collective effort and a combination of solutions. By taking action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, we can help to protect the planet and ensure a sustainable future for generations to come
Global warming is a complex and multifaceted problem, and there is no single solution that can address it entirely. However, here are five solutions that could help mitigate its effects:
Renewable Energy: One of the most effective ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions is to transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, geothermal, and hydroelectric power. These technologies have advanced significantly in recent years and are becoming more affordable and accessible.
Energy efficiency: Another approach is to increase energy efficiency by using energy-efficient appliances, improving insulation, and reducing wasteful practices. This would reduce the demand for energy and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Sustainable Agriculture: Agriculture is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable agricultural practices, such as reducing the use of fertilizers and pesticides, minimizing waste, and increasing soil health, can reduce the carbon footprint of food production.
Reforestation and afforestation: Trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in their biomass, making reforestation and afforestation effective ways to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions. This would also help to conserve biodiversity, improve air and water quality, and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Carbon pricing: Putting a price on carbon emissions through carbon taxes or cap-and-trade programs can incentivize businesses and individuals to reduce their emissions. This approach has been successful in countries like Sweden and Canada, where carbon pricing has helped to reduce emissions while also generating revenue for clean energy investments.

There are several ways in which humans can reduce the level of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Some of the most effective ways include:
Reducing energy consumption: Energy consumption is one of the largest sources of greenhouse gas emissions. By reducing energy consumption, individuals can significantly reduce their carbon footprint. This can be achieved by taking measures such as switching off lights and electronics when not in use, using energy-efficient appliances, and using public transportation, cycling, or walking instead of driving.
Transitioning to renewable energy: The use of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Governments and individuals can incentivize the use of renewable energy through subsidies, tax breaks, and other policies.
Improving energy efficiency: Improving the energy efficiency of homes, buildings, and industrial processes can reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. This can be achieved by using energy-efficient appliances, improving insulation, and optimizing industrial processes.
Reducing waste: Reducing waste can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions by reducing the need for landfills and incineration. This can be achieved by reducing the consumption of disposable products, recycling, composting, and reducing food waste.
Planting trees: Trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in their biomass. Planting trees can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change.
Using carbon capture technology: Carbon capture technology can capture carbon dioxide emissions from power plants and other industrial processes and store them underground or use them for other purposes. This technology is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
The top three sources of greenhouse gases are:
Burning of fossil fuels: The largest source of greenhouse gas emissions is the burning of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and gas. This releases carbon dioxide (CO2), which is the most prevalent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere.
Agriculture and livestock: Agriculture and livestock are responsible for emitting significant amounts of methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O), which are potent greenhouse gases. Methane is produced by enteric fermentation in ruminants such as cows and sheep, and from manure management. Nitrous oxide is produced by the use of nitrogen fertilizers and from animal waste.
Deforestation: Deforestation and other land-use changes, such as forest degradation, also contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, so when forests are destroyed or degraded, the carbon stored in the trees is released into the atmosphere as CO2.
The two most harmful greenhouse gases are:
Carbon dioxide (CO2): This is the most prevalent greenhouse gas and is responsible for about three-quarters of the warming effect caused by all greenhouse gases. CO2 is primarily emitted through the burning of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and gas, as well as through deforestation and other land-use changes.
Methane (CH4): Although methane is present in much smaller quantities than CO2, it is a much more potent greenhouse gas, with a warming potential over 20 times greater than that of CO2. Methane is primarily emitted by agriculture and livestock, as well as from the production and transport of fossil fuels, and from the decay of organic waste in landfills.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the gas that is most commonly associated with global warming and climate change, and it is widely considered to be the worst greenhouse gas in terms of its contribution to global warming. This is because it is the most abundant of the greenhouse gases and is released in large quantities by human activities such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation. Other greenhouse gases such as methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and fluorinated gases (e.g., HFCs, PFCs, SF6) also contribute to global warming, but they are generally less abundant and have shorter lifetimes in the atmosphere than carbon dioxide.